Modal Dialog
Suggest EditEmulation of a modal dialog box that appears on top of the main page content in response to user actions.
Description of Work
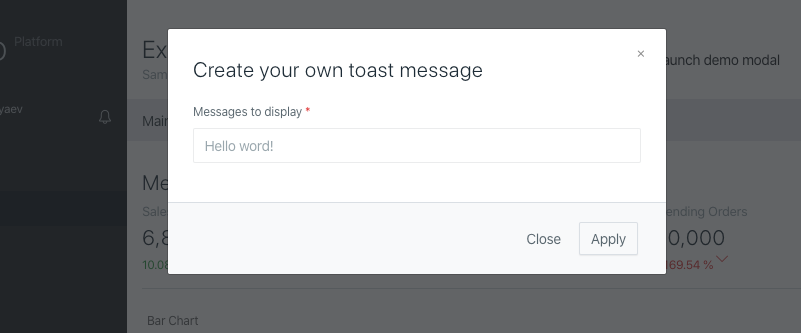
A modal window appears on top of the page, dimming it. This helps to focus the user’s attention on specific actions without losing the overall context. It is important to note that modal windows should not be used for large forms.
When to Use
Modal windows are best used for secondary content that is only needed in certain situations. This content may include settings, creating new documents, filling out small forms. For example, clicking on a link may open a modal window to enter an address.
Using
Modal windows can be implemented using a short syntax by calling a static method, which eliminates the need to create a separate class. The following example demonstrates how to create a modal window:
use Orchid\Support\Facades\Layout;
use Orchid\Screen\Actions\ModalToggle;
use Orchid\Support\Facades\Toast;
/**
* The screen's action buttons.
*/
public function commandBar(): array
{
return [
ModalToggle::make('Create notification')
->modal('toastModal')
->method('action')
->icon('full-screen'),
];
}
/**
* The screen's layout elements.
*/
public function layout(): array
{
return [
Layout::modal('toastModal', Layout::rows([
// ...
])),
];
}
/**
* The action that will take place when
* the form of the modal window is submitted
*/
public function action(): void
{
Toast::info('Hello, world! This is a toast message.');
}
It is important to note that when adding a modal window, it should be added at the top level of the array returned by the layout() method. It should not be added inside of another layout such as Tabs.
Warning. Avoid placing tables with filters, sorting, or pagination inside modal windows. These components use internal links for navigation, which will cause the modal to close when interacted with.
Title
To set the title of the modal window, the title method can be used:
Layout::modal('toastModal', Layout::rows([
// ...
]))
->title('Window title');
Passing Multiple Layouts
Sometimes a modal window may need to contain more than one layout.
In Orchid, you can pass an array of layouts directly to Layout::modal:
use Orchid\Screen\Layouts\Modal;
use Orchid\Screen\Layouts\Rows;
use Orchid\Screen\Fields\Input;
Layout::modal('notifModal', [
Layout::rows([
// Fields definition
]),
Layout::table('users', [
// Table columns definition
]),
]);
Window Size
Depending on the contents of the window, it may be necessary to resize it. This can be done by specifying the size method:
use Orchid\Screen\Layouts\Modal;
Layout::modal('toastModal', Layout::rows([
// ...
]))
->size(Modal::SIZE_LG);
Button Names
A modal window has two actions:
- Apply button – the default action; executes the method.
- Cancel button – closes the window without saving the entered data.
You can set your own names for them:
Layout::modal('toastModal', Layout::rows([
// ...
]))
->applyButton('Send')
->closeButton('Close');
Disabling Buttons
To disable each button has its own method:
Layout::modal('toastModal', [
Layout::rows([]),
])
->withoutApplyButton()
->withoutCloseButton();
Position
The modal window can be displayed, not only in the center of the screen, but also on the right side:
use Orchid\Screen\Layouts\Modal;
Layout::modal('toastModal', Layout::rows([
// ...
]))
->type(Modal::TYPE_RIGHT);
Opening
Sometimes you may need to open a modal window right after the page is displayed. To do this, you can use the ->open method:
use Orchid\Screen\Layouts\Modal;
Layout::modal('toastModal', Layout::rows([
// ...
]))
->open();
Deferred Data Loading
When working with a dataset, there is no need to create a modal window for each value. Instead, you can use deferred loading.
This will replace the query screen data when opening the window and display
new content.
In order to declare a modal window asynchronous, you must call the deferred method passing in the argument the method name that should be used instead of query:
Layout::modal('deferredModal', Layout::rows([
Input::make('welcome')
]))->deferred('loadDataOnOpen'),
Here is an example of a method for deferred loading:
/**
* This method is called to fetch data and is used to update the modal content
* when the modal is opened, without a full page reload.
*/
public function loadDataOnOpen(string $welcome): array
{
return [
'welcome' => $welcome,
];
}
When triggering the modal window, you can pass values directly:
use Orchid\Screen\Actions\ModalToggle;
ModalToggle::make('Open Modal')
->method('methodForSubmitModal')
->modalTitle('Customizable Title')
->modal('deferredModal', [
'welcome' => 'Hello world!',
]),
Disabling Reactive Processing
By default, the result of the window action will be displayed to the user on the screen, but this approach may not be suitable if you need to perform complex processing or download a file.
To disable response processing, you need to add a call to the rawClick method:
Layout::modal('toastModal', [
Layout::rows([]),
])
->rawClick();




